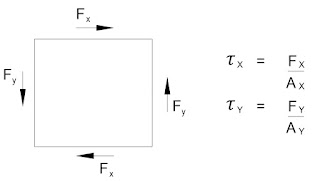
Ratio of shear stress to shear strain is called as 'Modulus of Rigidity'.
The Mechanical Engineering
Sunday, 24 December 2017
Friday, 30 June 2017
Wednesday, 28 June 2017
Poisson's Ratio
When a material is subjected to some force, its dimension changes in the direction of force applied. Due to the resulting effect of the longitudinal strain, a lateral strain (strain in the perpendicular direction of force applied) is also produced in the material.
This happens because of the constant mass of material i.e material quantity. Lateral dimension changes to sustain the constant amount of material.
The ratio of Lateral strain to Longitudinal strain is always constant for a particular material which is called 'Poisson's Ratio.' It is denoted by '𝒱'.
This happens because of the constant mass of material i.e material quantity. Lateral dimension changes to sustain the constant amount of material.
The ratio of Lateral strain to Longitudinal strain is always constant for a particular material which is called 'Poisson's Ratio.' It is denoted by '𝒱'.
Tuesday, 27 June 2017
Monday, 26 June 2017
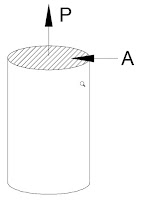
Stress in a Material
The internal; resistance offered per unit area by a material
towards the external forces applied is called ‘Stress’. Internal resistance
offered is equal to external forces applied on body.
Stress is denoted by 'σ '.
Stress ( σ ) = P/A
Where ‘P’ denotes the force applied &
‘A’ denotes the cross section area subjected the force P.
Friday, 16 June 2017
Factors Affecting Strength of Materials
a) Type of loading:-
Type of loading has very significant effect on strength of materials.
e.g
for a striaght bar of same material and same size (i.e same length, width and thickness), the load (W) bearing capacity will be higher in case (i) then that in case (ii)
b) Temperature:-
Temperature of material inversely affects its strength. Increase in temperature reduces the inter-molecular forces. Therefore the load bearing capacity of material reduces as the temperature is increased.
Type of loading has very significant effect on strength of materials.
e.g
for a striaght bar of same material and same size (i.e same length, width and thickness), the load (W) bearing capacity will be higher in case (i) then that in case (ii)
b) Temperature:-
Temperature of material inversely affects its strength. Increase in temperature reduces the inter-molecular forces. Therefore the load bearing capacity of material reduces as the temperature is increased.
Strength of Material
When some external forces are applied to a material, an internal resistance is shown by that material towards the external forces applied in order to prevent itself from cracks, breakages or permanent deformations.
In short it can be stated as 'The maximum resistance that is shown by a material towards the external forces applied is called Strength of Material.'
In short it can be stated as 'The maximum resistance that is shown by a material towards the external forces applied is called Strength of Material.'
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)